File Uploads
This documentation needs work. See "Help improve this page" in the sidebar.
Uploading files is now supported, see the release notes for more information: https://www.drupal.org/node/3024331
These two images show how to use postman to test file upload by JSON:API
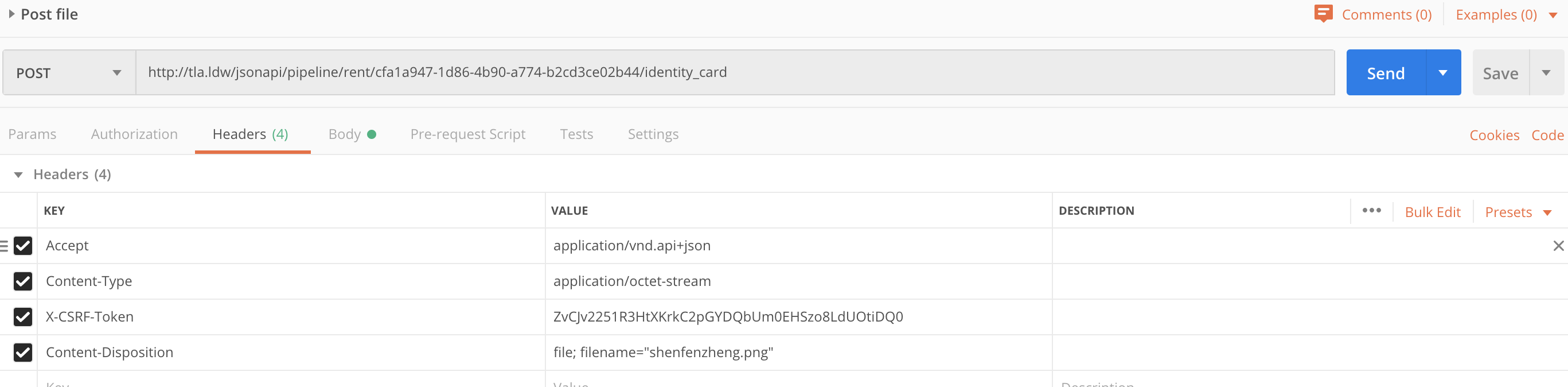
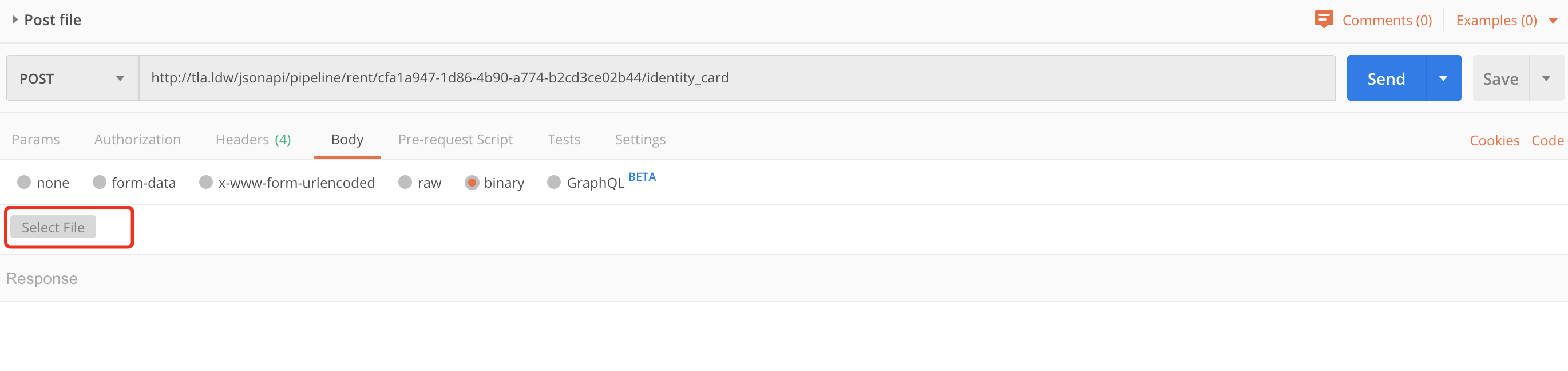
Curl example to upload a user picture
This assumes you've already authenticated and retrieved your CSRF token in another request.
curl -s -X POST -b cookie.txt \
--header "Accept: application/vnd.api+json" \
--header "Content-Type: application/octet-stream" \
--header "X-CSRF-Token: $TOKEN" \
--header 'Content-Disposition: file; filename="test.jpg"' \
--data-binary "@test.jpg" \
http://localhost/jsonapi/user/user/$UUID/user_pictureTips when using axios (or other http client libraries) and Node.js:
You may find that the format you have the data for an image that you need to post is in a Buffer format. For example:
<Buffer ff d8 ff e0 00 10 4a 46 49 46 00 01 01 00 00 01 00 01 00 00 ff fe 00 3e 43 52 45 41 54 4f 52 3a 20 67 64 2d 6a 70 65 67 20 76 31 2e 30 20 28 75 73 69 ... 582549 more bytes>
While this is technically the Buffer object representation of the binary image data, trying to send this to Drupal as the data parameter in your favorite http client library, like axios, will cause you to create an incorrect file. A file will be there, you will get back a successful response, but the image will probably just be a white square on a black background.
You will be required to use the Node.js Buffer class to convert this to an actual binary Buffer output. Specifically, you will use the from method
For example:
Let's say we have retrieved a file object using the AWS S3 SDK and retrieved the Body of that file object. That Body will have Buffer data like what is shown above. Let's put that Body data into a variable, use the Buffer class to get it into the correct format and send it along to Drupal's JSON:API endpoint using axios (note: this snippet is just the important part of the code not the entire handler. Also, we usually split all this up into some helper libraries to keep things more DRY). The important line is data: Buffer.from(buffer, "binary"):
const buffer = storedFile.Body; // contains the buffer data indicated above.
const drupalData = await axios({
method: "post",
url: url, //URL to /jsonapi/media/image/field_media_image/ on your site.
auth: {
username: xxx
password: xxx
},
headers: {
'Accept': 'application/vnd.api+json',
'Content-Type': 'application/octet-stream',
'X-CSRF-Token': token, // You will need to retrieve this from Drupal first from /session/token!
'Content-Disposition': 'file; filename="' + filename + '"',
},
data: Buffer.from(buffer, "binary"),
});
console.log(drupalData); // the uuid if the newly created file is contained in drupalData.data.idThis is particularly helpful if you are using Node.js AWS Lambda functions and pulling files out of S3 to post to Drupal.
Help improve this page
You can:
- Log in, click Edit, and edit this page
- Log in, click Discuss, update the Page status value, and suggest an improvement
- Log in and create a Documentation issue with your suggestion
 Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.
Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.









