Drupal.org is brought to you in part by the generous support of sponsors like:
Translating content
In Drupal, the main method for translating content is to use the core Content Translation module, which has an approach very similar to the Drupal 7 "Entity Translation" module. Only a single node or entity is created. The entity is language-independent. Only the associated fields are flagged with a language.
Enable content translation
To enable content translation in Drupal, enable the core "Content Translation" module.
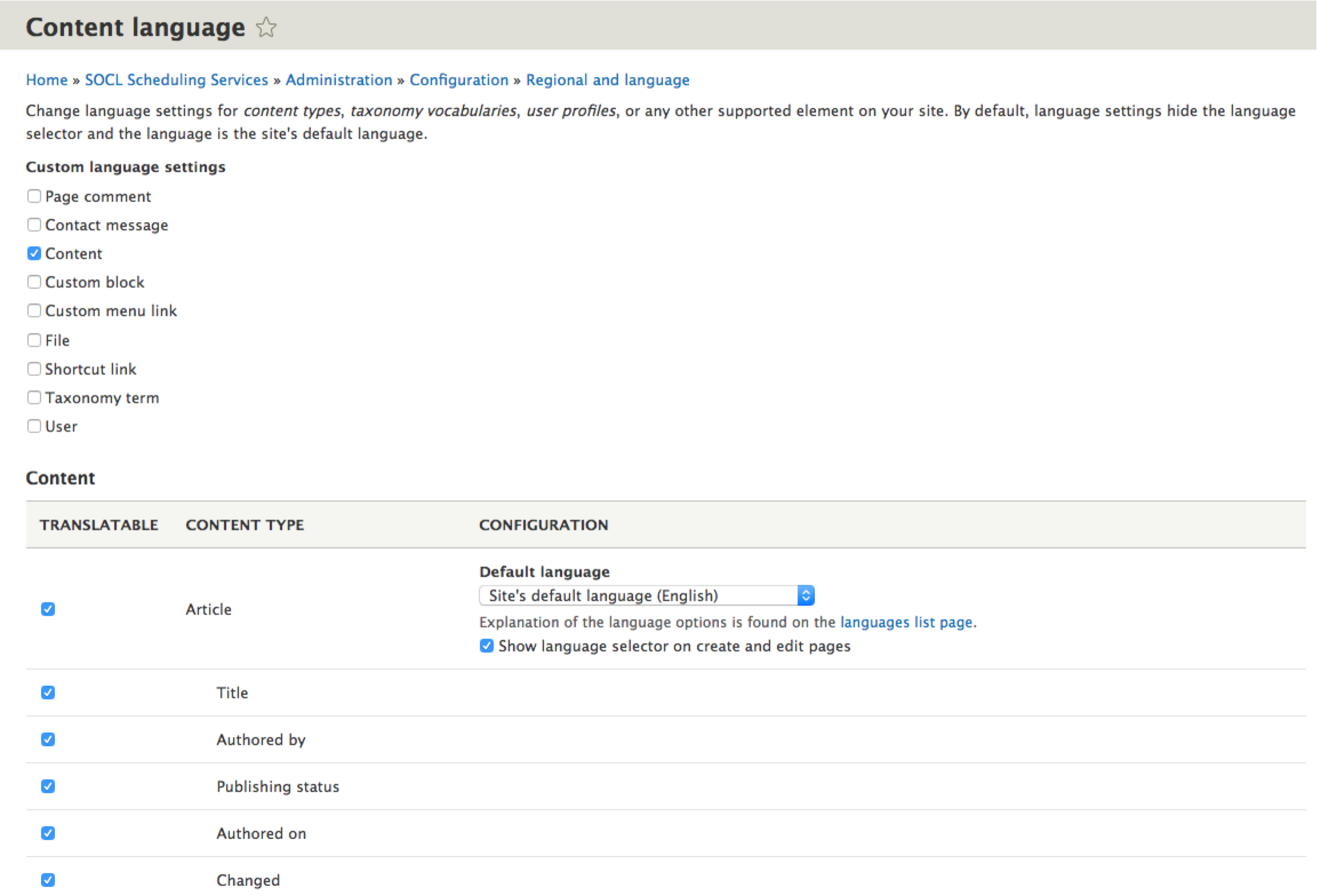
To configure: Configuration > Content language and translation ( admin/config/regional/content-language )
This module allows you to decide whether each type of content entity (node pages, comments, custom blocks, taxonomy terms, user accounts, etc.) should be translatable or not. Then, within each entity type, you can decide whether the sub-types (content types for node page content, terms in particular vocabularies for taxonomy, etc.) should be translated. And within each translatable entity sub-type, you can decide which fields should be translatable.
To Translate content:
Once you have designated certain fields of certain entity sub-types to be translatable, and you've installed at least two languages on your site, you can translate content items.
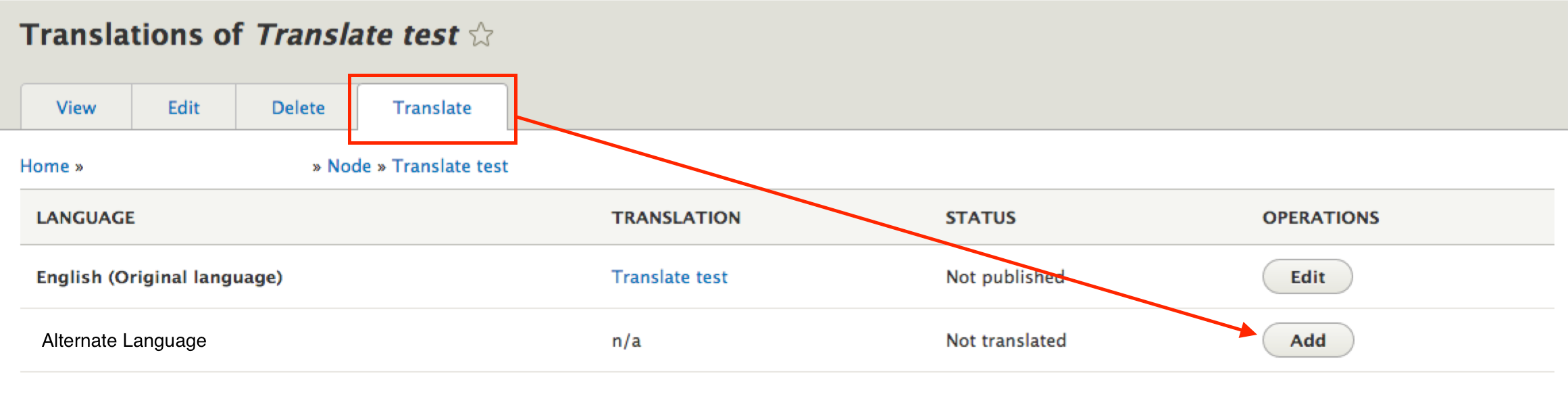
Users with translate permissions will see links to "Translate" alongside where you'd normally see "Edit" links, and you'll be able to add translations for each configured language.
Behind the scenes, you'll see that all the translations share the same ID (such as the node ID), and if you look at the Drupal database, you'll see that there is a table that stores information about each translation (such as the language and the node ID), and then each field stores its translated values in a separate table.
 Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.
Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.










