On this page
Plugin Contexts
Sometimes plugins require another object in order to perform their primary operation. This is known as plugin context. Using a practical example, almost all condition plugins require a context. Let's look at the NodeType condition's plugin definition.
/**
* Provides a 'Node Type' condition.
*
* @Condition(
* id = "node_type",
* label = @Translation("Node Bundle"),
* context_definitions = {
* "node" = @ContextDefinition("entity:node", label = @Translation("Node"))
* }
* )
*
*/
There are 3 keys in this plugin definition, first is the required 'id', next a 'label' for the user interface, and finally a 'context_definitions' array. The context_definitions key stores an array of named context definitions the condition requires in order to perform its "evaluate()" method. In the case of the NodeType condition, we must have a node in order to check its type. The NodeType::evaluate() method demonstrates how this works in practice:
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function evaluate() {
if (empty($this->configuration['bundles']) && !$this->isNegated()) {
return TRUE;
}
$node = $this->getContextValue('node');
return !empty($this->configuration['bundles'][$node->getType()]);
}
The ContextAwarePluginBase::getContextValue() method takes a name that corresponds to the key documented in the context array of the plugin definition. The plugin definition documents that this must be a node entity (leveraging typed data syntax). Any typed data syntax definition is supported. The ContextDefinition annotation passes through to the ContextDefinition class. The first string passed to the ContextDefinition annotation is the typed data plugin id you wish to require. This string is passed directly without an associated key. All subsequent parameters must be passed with their associated keys. As shown in the NodeType condition, the label for the context definition is clearly documented with a 'label' key. Supported keys include:
- label
- required
- multiple
- description
- default_value
- class
Required is true by default; multiple is false by default. Default value is NULL by default, and the class will default to the \Drupal\Core\Plugin\Context\ContextDefinition class. If you supply your own class, you must implement the \Drupal\Core\Plugin\Context\ContextDefinitionInterface interface. Annotations should likely not leverage the default_value key.
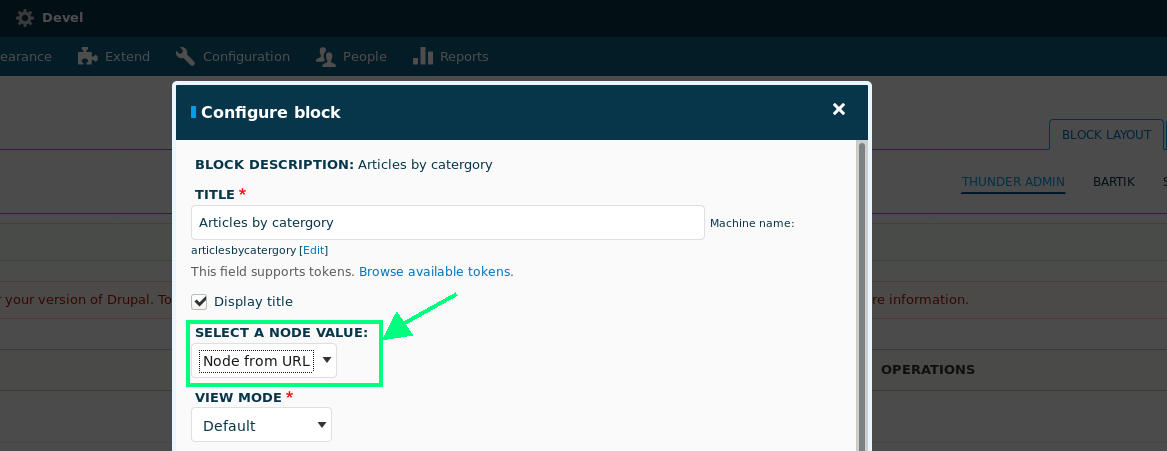
Context on blocks
When you are adding node context_definitions to custom blocks don't forget to select where to provide those nodes from on block config form.
Context Aware Custom Plugin Types
This is about defining the 'context_definitions' for a custom plugin type which was created by implementing a custom plugin manager, custom annotation class and a custom plugin interface. While the context_definitions are the same, some additional steps need to be followed to get the contexts working for the custom plugin type. These are the steps:
- The plugin base class should extend the 'Drupal\Core\Plugin\PluginBase' class and should implement 'Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginInterface' (for specifying the context awareness methods) as well as 'Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContainerFactoryPluginInterface' (for ensuring dependency injection). Also, it should use the traits 'Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginTrait' and 'Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginAssignmentTrait' which implement the context awareness methods.
- Using the 'create' static setter method, inject the 'context.repository' service as follows:
/** * {@inheritdoc} */ public static function create(ContainerInterface $container, array $configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition) { return new static( $configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition, $container->get('context.repository') ); } - Implement the constructor as follows, to assign the contextRepository argument to the class property by the same name. In addition, call the custom method 'setDefinedContextValues()' which would assign the plugin contexts with runtime data. (Implementation details of the 'setDefinedContextValues()' method is given further down).
/** * {@inheritdoc} */ public function __construct(array $configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition, ContextRepositoryInterface $contextRepository) { $this->contextRepository = $contextRepository; // Pass the other parameters up to the parent constructor. parent::__construct($configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition); // set the defined contexts' values $this->setDefinedContextValues(); } - Implement the custom method 'setDefinedContextValues()' as follows, which fetches the runtime contexts from the 'context.repository' service and assigns them to the plugin defined contexts, thereby making them available to the plugin.
/** * Set values for the defined contexts of this plugin * */ private function setDefinedContextValues() { // fetch the available contexts $available_contexts = $this->contextRepository->getAvailableContexts(); // ensure that the contexts have data by getting corresponding runtime contexts $available_runtime_contexts = $this->contextRepository->getRuntimeContexts(array_keys($available_contexts)); $plugin_context_definitions = $this->getContextDefinitions(); foreach ($plugin_context_definitions as $name => $plugin_context_definition) { // identify and fetch the matching runtime context, with the plugin's context definition $matches = $this->contextHandler() ->getMatchingContexts($available_runtime_contexts, $plugin_context_definition); $matching_context = reset($matches); // set the value to the plugin's context, from runtime context value $this->setContextValue($name,$matching_context->getContextValue()); } }
Once the above are done, the contexts can be accessed inside the plugin class's methods by calling the getContextValue() method, as below:
// node route context
$node = $this->getContextValue('node');
// current user context
$user = $this->getContextValue('user');Putting everything together, the full code for the plugin base class is as follows:
namespace Drupal\your_module;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\PluginBase;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginTrait;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContextAwarePluginAssignmentTrait;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\ContainerFactoryPluginInterface;
use Symfony\Component\DependencyInjection\ContainerInterface;
use Drupal\Core\Plugin\Context\ContextRepositoryInterface;
/**
* Base class for your custom plugins.
*/
abstract class YourModulePluginBase extends PluginBase implements ContextAwarePluginInterface, ContainerFactoryPluginInterface, YourModulePluginInterface {
use ContextAwarePluginTrait;
use ContextAwarePluginAssignmentTrait;
protected $contextRepository;
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public static function create(ContainerInterface $container, array $configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition) {
return new static(
$configuration,
$plugin_id,
$plugin_definition,
$container->get('context.repository')
);
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function __construct(array $configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition, ContextRepositoryInterface $contextRepository) {
$this->contextRepository = $contextRepository;
// Pass the other parameters up to the parent constructor.
parent::__construct($configuration, $plugin_id, $plugin_definition);
// set the defined contexts' values
$this->setDefinedContextValues();
}
/**
* {@inheritdoc}
*/
public function label() {
// Cast the label to a string since it is a TranslatableMarkup object.
return (string) $this->pluginDefinition['label'];
}
/**
* Set values for the defined contexts of this plugin
*
*/
private function setDefinedContextValues() {
// fetch the available contexts
$available_contexts = $this->contextRepository->getAvailableContexts();
// ensure that the contexts have data by getting corresponding runtime contexts
$available_runtime_contexts = $this->contextRepository->getRuntimeContexts(array_keys($available_contexts));
$plugin_context_definitions = $this->getContextDefinitions();
foreach ($plugin_context_definitions as $name => $plugin_context_definition) {
// identify and fetch the matching runtime context, with the plugin's context definition
$matches = $this->contextHandler()
->getMatchingContexts($available_runtime_contexts, $plugin_context_definition);
$matching_context = reset($matches);
// set the value to the plugin's context, from runtime context value
$this->setContextValue($name,$matching_context->getContextValue());
}
}
}Help improve this page
You can:
- Log in, click Edit, and edit this page
- Log in, click Discuss, update the Page status value, and suggest an improvement
- Log in and create a Documentation issue with your suggestion
 Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.
Support for Drupal 7 is ending on 5 January 2025—it’s time to migrate to Drupal 10! Learn about the many benefits of Drupal 10 and find migration tools in our resource center.









